如何快速计算Android进程模块自身的加载基地址?
缘起
在Android安全开发中,经常需要获取进程内模块的加载基地址,获取方法一般有:
- 通过解析/proc/pid/maps文件
- 使用“dl_iterate_phdr”遍历
上述这些方法比较慢,用于一些检测任务是可以的,考虑这样一个场景:开发一个安全模块,这个模块是接管了进程的入口,在入口处需要基于安全模块自身的加载基地址做一些事情,如检验、取数据等。那么快速获取基地址就变得非常有必要了。
探索
在阅读android 8.1.0_r33中的linker源码时(bionic/linker/linker_main.cpp),发现一段非常有意思的代码:
1 | extern "C" ElfW(Addr) __linker_init(void* raw_args) { |
这两行神奇的代码可直接计算出linker的加载基地址,如果我们直接使用来计算自己开发的模块加载基地址,结果会是0。为什么呢?其实上面代码片段中的注释已经解释了原因,如果代码在未完成重定位之前就执行,就能计算出正确的基地址,但自己开发的模块执行这两句代码时候,已经完成了重定位,所以结果是0。
为了更好地理解重定位前后对计算结果的影响,需要考察这两句代码对于的汇编语言,这里假设linker加载基地址是0xea923000。
1 | 0000f6c0 <__dl___linker_init>: |
linktime_addr的偏移是0x8B1B0。在重定位之前,地址0x8B1B0的值也是0x8B1B0。
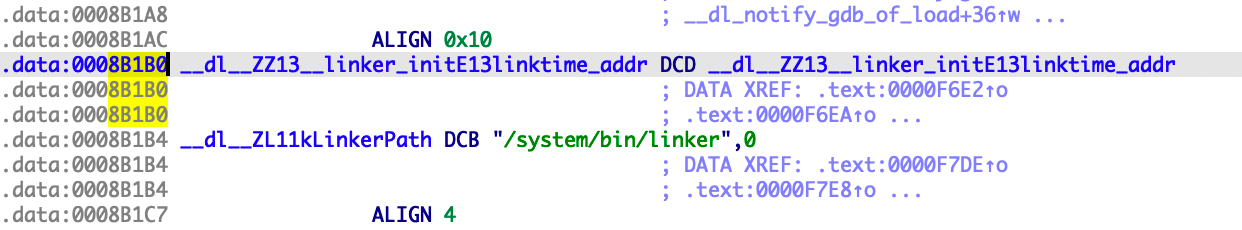
使用readelf工具考察linker中的重定位项:
1 | $ arm-linux-androideabi-readelf -r linker |
继续观察R_ARM_RELATIVE类型的重定位如何处理(6.0.1_r10/bionic/linker/linker.cpp):
1 | case R_GENERIC_RELATIVE: |
由于0x0008b1b0在重定位表里且类型为R_ARM_RELATIVE,完成重定位之后,地址0x8B1B0的值变为0xEA9AE1B0(0x8B1B0+0xEA923000),与0xEA9AE1B0(linktime_addr变量在内存的地址)相减为0。这就是为什么在我们编写的模块里无法使用此种方法完成加载基地址的计算。
难道就这样结束了?不,虽然这种方法无法被直接使用,但这种思路值得借鉴,稍加改进之后,就可以运用到自己的方案中。改进方法:想办法去掉重定位项。
改进
为了避免生成重定位项,可通过汇编语言实现,下面是模块文件结构:
1 | sample |
文件Application.mk
1 | APP_ABI := armeabi |
文件Android.mk
1 | LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir) |
文件asm.h
1 |
|
文件begin.S
1 | #include "asm.h" |
文件sample.c
1 |
|
反汇编构建出来的libsample.so中的_init函数:
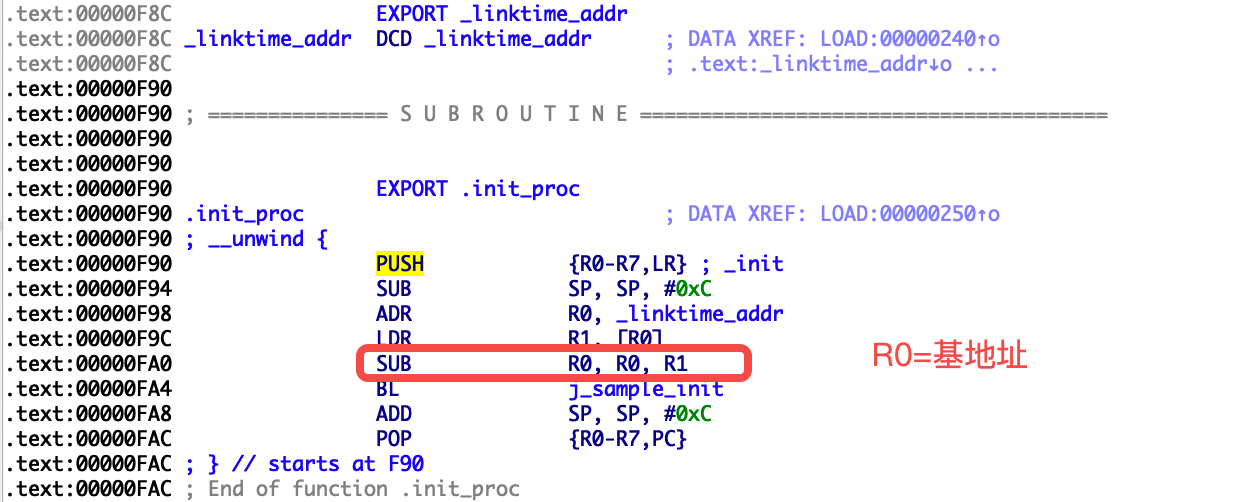
你可能已经注意到linktime_addr的初始值被设为0xf8c,这里只是方便演示,在笔者本机编译发现linktime_addr的地址是0xf8c。在实际运用中,你应该编写一个独立的脚本专门patch模块中linktime_addr的值,比如通过解析ELF文件,获得linktime_addr在文件的位置,并在此位置写入对应的值即可。
小结
本文通过研究linker中计算模块基地址的方法,找到了一种可快速计算模块自身的加载基地址。